Student Rights in Education
BC Children and youth have rights in the K-12 education system. These are outlined in the BC School Act, Orders In Council, Ministerial Orders, and policy.
Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD):
Canada ratified the United Nations Convention on the Rights of People with Disabilities (CRPD) in 2010.
The CRPD is an international human rights treaty aimed at protecting the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities without discrimination and on an equal basis with others.
Parties to the CPRD are required to promote and ensure the full enjoyment of human rights of persons with disabilities including full equality under the law.
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC):
The UNCRC is a human rights treaty created by the United Nations that provides a full list of rights for all children up to the age of 18.
Almost every country in the world has signed the Convention. Signing the Convention means these countries promise to protect and promote these rights. Canada signed the convention in 1991. The Convention says that governments are in charge of making sure that children’s rights are respected and that children know about their rights.
Student rights under the UNCRC:

- The right to free and compulsory primary education,
- to equal access to secondary and higher education, and
- to school discipline consistent with the child’s human dignity.
[Article 28]

- The right to express their views freely in matters that affect them, and
- to have their views considered in accordance with their age and maturity.
[Article 12]
United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP):
UNDRIP addresses the most significant issues affecting indigenous peoples
– their civil, political, social, economic and cultural rights.
It also bears on their right to self-determination, spirituality, language, lands, territories, resources and free, prior and informed consent.
Orders in council:
“Students have the opportunity to avail themselves of a quality education consistent with their abilities, the opportunity to share in the shaping of their educational programs, and the opportunity to determine their career and occupational goals.
They have the responsibility to make the most of their opportunities, to respect the rights of others, and to cooperate with fellow students in the achievement of their goals.”
[Statement of Education Policy Order, Order in Canada 1280/89]

Student Rights under the School Act:
Students have a right to attend public school from the year they reach the age of five until the end of the school year in which they turn 19. 2(1)
Students who are residents of BC have a right to enrol in any public school in any of BC’s 60 school districts, subject to space availability.
Catchment areas for each public school are determined by boards of education and the right to attend a catchment area school is set out in the School Act Section 74.1 and the policies of local boards. 2(2)
Consult with a teacher, principal, vice principal, or director of instruction about their educational program. 4
Appeal a decision of an employee of a board, or failure to make a decision, if it significantly affects the education, health, or safety of a student, within a reasonable time from date that the parent, guardian, caregiver or student was informed of the decision. 11
They may enrol in public school, independent school, a francophone education authority school if they meet the entitlement criteria, a Provincial school, a school operated by a First Nation or Community Authority, a school operated by the government of Canada, or a K-12 educational program provided by a First Nation under its own laws.
They may also register as a home schooler under Section 13 of the School Act.
They may cross-enrol in other programs offered by an independent school authority or francophone education authority (if they are already enrolled in a francophone education authority school), if the other programs are in whole or part delivered through online learning.
Rights under other legislation and agreements:
Students with rights under Section 23 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms have the right to attend an educational program provided in French.
First Nations students may attend a school operated by the government of Canada or by a First Nation under the First Nations Jurisdiction over Education in British Columbia Act (Canada).
Learn more:
- United Nations, Convention on the Rights of the Child
- The Children’s version by Unicef
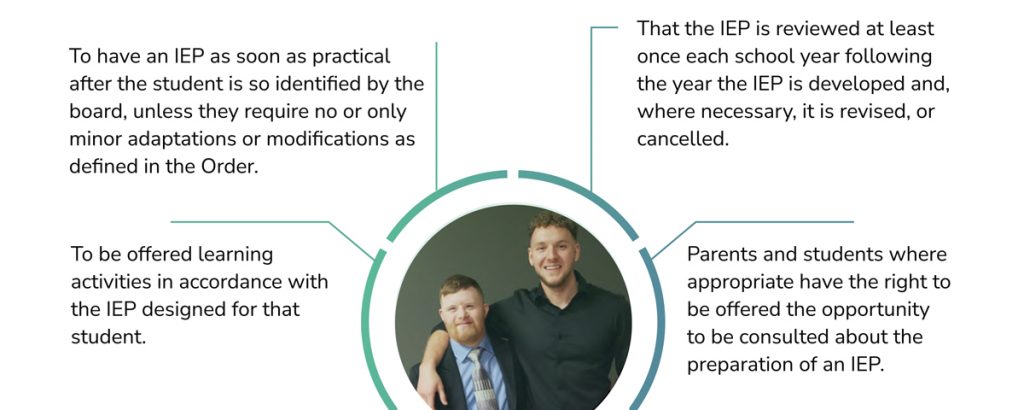
- Individual Education Plan Order M638/95 (PDF)
- School Act
- Statement of Education Policy Order – Lieutenant Governor Order in Council (PDF)
- Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms – Section 23
- First Nations Jurisdiction over Education in British Columbia Act

By Family Support Institute of BC & BCEdAccess